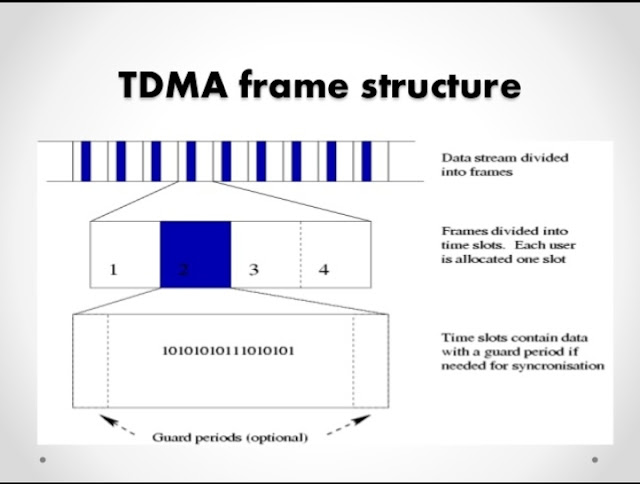
TDMA T ime D ivision M ultiple A ccess (TDMA) : a digital wireless telephony transmission technique. TDMA allocates each user a different time slot on a given frequency. TDMA divides each cellular channel into three time slots in order to increase the amount of data that can be carried. TDMA technology was more popular in Europe, Japan and Asian countries, where as CDMA is widely used in North and South America. But now a days both techologies are very popular through out of the world. Advantages of TDMA: TDMA can easily adapt to transmission of data as well as voice communication. TDMA has an ability to carry 64 kbps to 120 Mbps of data rates. TDMA allows the operator to do services like fax, voice band data, and SMS as well as bandwidth-intensive application such as multimedia and video conferencing. Since TDMA technology separates users according to time, it ensures that there will be no interference f...

